USB Cables – and Why They're Important
Read Time: Approx. 14 min.

From A to Z: Understanding USB Cable Types and Their Functions
Everyone knows what USB is nowadays – but how much do you really know? I bet the vast majority of people don’t even know what USB really stands for. We’ll get to that, but the fact remains that USB is so common in today’s tech world that we don’t even think about it. That’s a good and bad thing, but its commonality also means that it’s important. We’re here today to tell you why USB cables are important – especially when it comes to transmitting the data of your music.
Cables are the connection point from point A to point B, and when considering music (especially high-resolution audio that can include very large file sizes), if your music data isn’t getting to where it needs to go, that doesn’t bode well for the quality of audio you might get on the receiving end. Some people will just say that it's 1s and 0s. However, the overall quality of your digital cables can affect the sound quality of your music just like analog cables. Before we get into the issues of quality and materials, let's start from the beginning and go over some basics about USB cables. They come in varying shapes, sizes, connectors, lengths, and more, and it can be confusing to understand the differences. So, what's the deal with USB Cables?
USB Audio Cables: Why They're Important
What Devices Use A USB Cable?
Q: What does USB stand for?
A: USB stands for Universal Serial Bus. It remains one of the most common connection options for electronic devices today. It is commonly found on computers, peripherals, and consumer devices. USB can be used for data transfer or device charging purposes.
Q: What are the different types of USB cables?
A: USB cables come in many different variations of connectors, which determine the data transfer speed and charging capacity threshold of the cable. Learn more about the generational upgrades of USB 1-4 below.
Q: What is Universal about USB?
A: Same connector type cables are all backward compatible, no matter the USB generation. For example, a USB 4.0 Type A cable will work in a USB 2.0 port and vice versa. However, you won't experience USB 4.0 transfer speeds in a 2.0 port, but the cable will still be able to transfer data (speed is limited by port/source USB generation).
A: USB stands for Universal Serial Bus. It remains one of the most common connection options for electronic devices today. It is commonly found on computers, peripherals, and consumer devices. USB can be used for data transfer or device charging purposes.
Q: What are the different types of USB cables?
A: USB cables come in many different variations of connectors, which determine the data transfer speed and charging capacity threshold of the cable. Learn more about the generational upgrades of USB 1-4 below.
Q: What is Universal about USB?
A: Same connector type cables are all backward compatible, no matter the USB generation. For example, a USB 4.0 Type A cable will work in a USB 2.0 port and vice versa. However, you won't experience USB 4.0 transfer speeds in a 2.0 port, but the cable will still be able to transfer data (speed is limited by port/source USB generation).
USB Stands for “Universal Serial Bus” and is the most common connection protocol for electronic devices today. It’s able to fulfill a number of different tasks such as transmitting data and charging. You probably have nearly hundreds of cables lying around your house and have likely thrown a lot away over the years. They come with everything – computers, phones, headphones, wireless speakers, tablets, toys with rechargeable batteries, game consoles. Most computers and electronic devices have some form of USB connection, and it has become a standard for companies to ship cables with their products.
The USB protocol has been updated over time since its creation, resulting in faster data transfer and charging speeds. This has also resulted in a plethora of different USB cable connectors and it can be challenging to figure out what does what. Even though two cables might be USB cables, they can look completely different and also have varying performance.
We'll go over the differences in connectors and types of USB cables in a minute, but these connector variations also affect what devices are compatible with the cables. Of course, you can always get adapters, but you'll still be constrained by the specs of the cable itself rather than the connectors and/or adapters. Some ports on older devices will not be compatible with newer cables, or charging speeds might take much longer if the cable is an older version or the connected power adapter doesn't produce enough wattage for the devices' specifications. So let's start breaking it down - everything you ever wanted to know about USB cables and why they matter.
What are the Different Types of USB Cables?
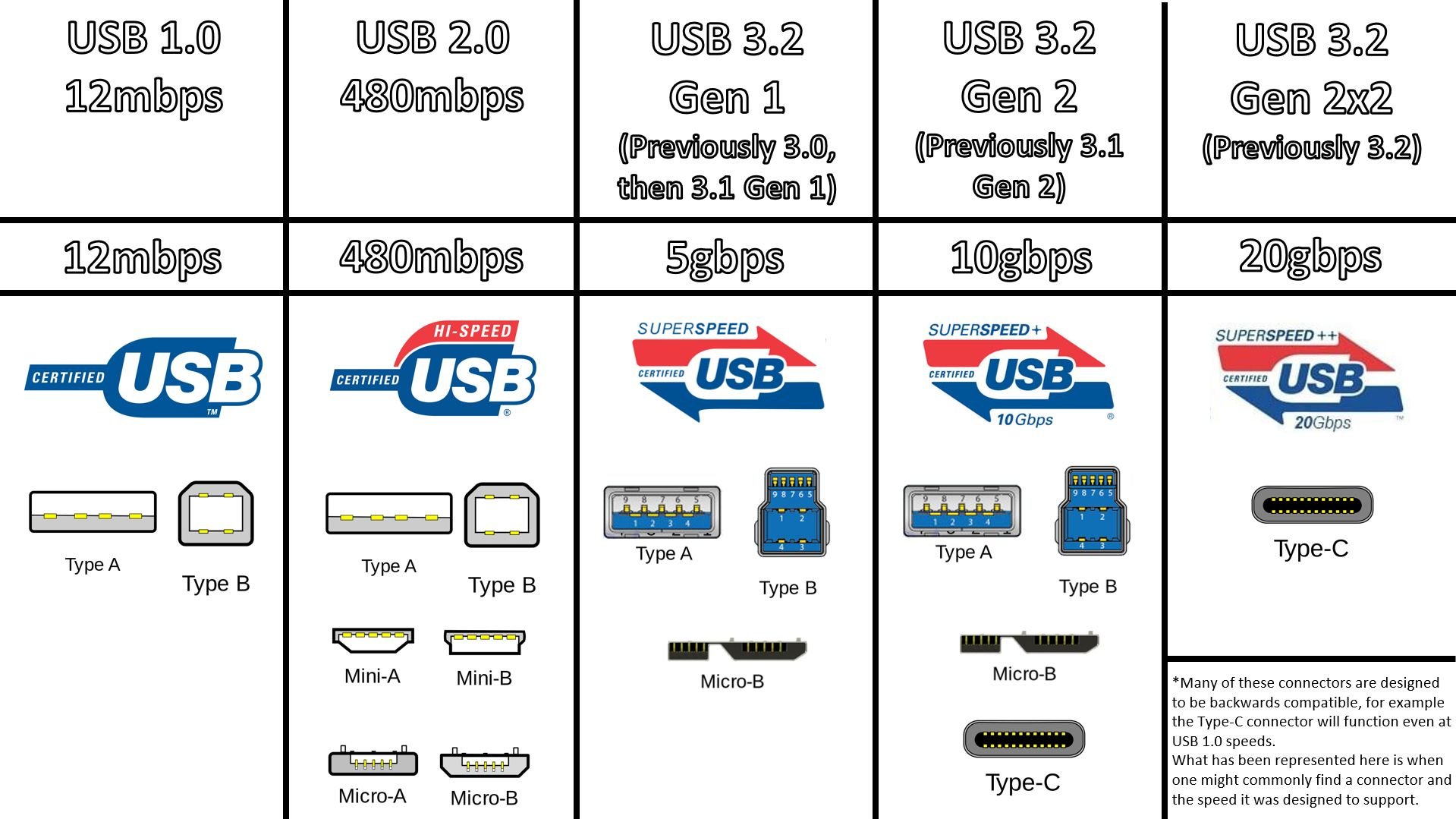
It's ironic in a way that there are so many cable types and variations despite being a "Universal" serial bus. Like all things, USB technology has improved over time, but it all started somewhere. Here we'll go over the generations of USB and how the data transfer and charging speeds have improved from one generation to the next.
It's ironic in a way that there are so many cable types and variations despite being a "Universal" serial bus. Like all things, USB technology has improved over time, but it all started somewhere. Here we'll go over the generations of USB and how the data transfer and charging speeds have improved from one generation to the next.
USB Cable Generations / Speed Standards
-
USB 1.0 is the first generation of USB Type-A connectors. The max data transfer speed is 12Mbps and charging power up to 15W. The first generation of USB specs are tremendously slow by today's standards, but will still work with the latest USB data ports if you don't need fast transfer speeds. That's the beauty of backward compatibility for the USB standard. USB 2.0 has a max data transfer speed of 480Mbps and supports lengths up to 5m. The max charging power for USB 2.0 is typically up to 15W. USB 2.0 is still widely used today, though it is getting phased out by 3.0 quickly.
-
USB 2.0 has a max data transfer speed of 480Mbps and supports lengths up to 5m. The max charging power for USB 2.0 is typically up to 15W. USB 2.0 is still widely used today, though it is getting phased out by 3.0 quickly.
- USB 3.0 (or 3.2) comes in 3 variations. Gen 1 has a max data speed of 5Gbps and usually tops out with 3m cable lengths. Max charging power is typically up to 15W. Gen 2 USB 3.2 maxes out data speeds at 10Gbps but only allows for 1m cable lengths. Max charging power however can go up to 100W with compatible chargers. Gen 2x2 USB 3.2 maxes at 20Gbps data transfer speeds. USB 3.0 is currently the most popular version today and is standard on most computers.
- USB 4.0 is new and rolling out to more devices, but you'll see an average data speed of 40Gbps and max charging power of 100W with compatible chargers (the same specs as Thunderbolt). It's still in the early phases of being rolled out as it's quite new to the market. Expect USB 4.0 to really start making an appearance by the end of 2024 (estimated at the time of writing this blog).
What is Universal About USB Cables?
The thing that really makes the USB 'universal" is backward compatibility. Many cables are designed to be device-specific, but backward compatibility technically applies to ports rather than the cables. If you connect a USB 2.0 cable to a USB 3.0 port, you will be limited by the connection protocol of the source and the receiver. If both the source and receiver are both 3.0, then you'll get USB 3.0 speeds. If the source is 3.0 but the receiver is 2.0, then you'll be capped by the receiver's ability to transfer at USB 2.0 speeds. This is an important distinction to make so you don't expect a USB 2.0 hard drive to magically start transferring at USB 4.0 speeds if you have the port.
The thing that really makes the USB 'universal" is backward compatibility. Many cables are designed to be device-specific, but backward compatibility technically applies to ports rather than the cables. If you connect a USB 2.0 cable to a USB 3.0 port, you will be limited by the connection protocol of the source and the receiver. If both the source and receiver are both 3.0, then you'll get USB 3.0 speeds. If the source is 3.0 but the receiver is 2.0, then you'll be capped by the receiver's ability to transfer at USB 2.0 speeds. This is an important distinction to make so you don't expect a USB 2.0 hard drive to magically start transferring at USB 4.0 speeds if you have the port.
This effectively means that the cables themselves aren't capped at specific USB transfer speeds when it comes to their materials and geometries. It has more to do with the connector(s) on the cable and the USB ports on both the source and connecting device that you are connecting the cable to. Bottom line: if you have different USB protocols your transfer and charging speed will always be limited by the older generation port or device.
The USB technology evolves, the clearest way to see that is by the connectors on the cables. As the tech improves, so do the specs, so let's see how transfer and charge speeds change with each generational update.
USB Connector Types: How to Decipher Them
Q: What types of USB cables are there?
A: The three most common types of USB cables are type A, B, and C. Type A USB cables are the most common and oldest. Type C USB cables are the new standard in transfer speeds and device charging.
Q: Are USB Audio cables different from regular USB cables?
A: Yes. USB Audio cables are not meant for fast and larger data transfers. They are made with fewer conductors to only prioritize the transfer of audio data. This means that USB Audio cables should only be meant to connect your audio source to your audio gear.
Q: What is the most important thing about a USB Cable?
A: The most important thing about USB is the geometry of the cable itself: the quality, length, shielding, and more. Long cable lengths produce a larger resistance, so the shorter the cable the less distance the data has to run and therefore the less resistance it encounters. Shielding is important to keep external noise and interference out of your audio signal.
A: The three most common types of USB cables are type A, B, and C. Type A USB cables are the most common and oldest. Type C USB cables are the new standard in transfer speeds and device charging.
Q: Are USB Audio cables different from regular USB cables?
A: Yes. USB Audio cables are not meant for fast and larger data transfers. They are made with fewer conductors to only prioritize the transfer of audio data. This means that USB Audio cables should only be meant to connect your audio source to your audio gear.
Q: What is the most important thing about a USB Cable?
A: The most important thing about USB is the geometry of the cable itself: the quality, length, shielding, and more. Long cable lengths produce a larger resistance, so the shorter the cable the less distance the data has to run and therefore the less resistance it encounters. Shielding is important to keep external noise and interference out of your audio signal.
What Types of USB Cables Are There?
There are a variety of USB connector types, and they can sometimes be indicators of what generation device they go with depending on the design, color, and connector type. It's not always so cut and dry, however.
There are a variety of USB connector types, and they can sometimes be indicators of what generation device they go with depending on the design, color, and connector type. It's not always so cut and dry, however.
USB TYPE-A: In the early days of USB, the most common connector was USB Type-A (and still is the most common type today). This is the rectangular-shaped connector that fits into most portable wall chargers, computer ports for peripherals and devices, and more. It is typically a white or gray color on the inside of the connector. The Type-A standard has been around for years, and it's not until recently that it's being phased out by USB-C which we'll talk about in a minute. You can find Type-A connectors across all USB generations. USB 1.0-2.0 - You can find Micro-A and Mini-A variants which provide the same performance but have smaller connectors. These have been phased out mostly with Micro-B and Mini-B in USB 3.0 applications.
USB TYPE-B: Type-B connectors are larger connectors, nearly square-shaped, and were common with older computer peripherals like printers and such. The USB 3.0 version had an additional notch at the top and was colored blue. USB 3.0-3.1 Micro-B (or micro-USB) connectors were popular with external hard drives and had an additional notch for the pinout, but these are now being replaced by the more popular and newer USB-C connectors.
Both early Type-A and B (USB 1 and 2.0) came in a mini and micro variant, offering a smaller-sized connector (Mini-A, Mini-B, Micro-A, Micro B). The smaller Type-A versions were less common than the Type-B, and for a time were the new standard over their larger connector counterparts. Once the USB Standard graduated to gen 3.0 the Type-A connectors got a makeover with a blue PCB indicating it was the newer USB 3.0 as opposed to the white of USB 1.0 and 2.0. You'll find blue on both USB-A cables and the even larger Type-B USB 3.0 connectors. The micro and mini variants also did away with the Type-A versions, leaving Mini-B and Micro-B to dominate.
USB TYPE-C: The latest standard for USB connection is the Type-C connector. There are a lot of great things about the newer connector from the fact that it's smaller than previous USB type connectors and it's also double-sided, meaning you can connect it properly from either side. With types A and B, there is a specific configuration in order for the connection to be made. Type-C cables and connectors can also provide and receive more power than previous USB versions, as well as output display data to a monitor, and be used specifically for USB PD (power delivery) applications. USB-A devices (USB Type-A) are often used with adapters to update the compatibility to USB-C.
The other convenient thing about USB-C being a smaller, more powerful, and compatible connector type is that the connection slot takes up much less room on devices. Laptops specifically have been adopting the port for this very reason. We'll also see cable types like Thunderbolt and Lightning connectors, but for the sake of this blog, we'll only focus on the USB standard. We'll see lots of similarities between charging and data transfer speeds between Thunderbolt 3&4 and USB 4.0. USB-C Charging is common for device charging today - from car chargers for your iPhone 15, MacBook Pro, and all popular phone chargers now.
NOTE: USB Protocol is common on both MAC and Windows computers. The USB generation of your computer will depend on its age - and which USB generation was most prevalent at the time it was manufactured. It is also common for newer computers and laptops to have multiple port types (for example both USB Type A and Type C ports). Although newer and smaller laptops have opted for the USB-C port for its smaller port size. This has made the usage of USB adapter cables and converters commonplace, though, in the case of USB audio, the usage of adapters will not affect the data transfer rates. It is always recommended that you connect your music source directly to your audio equipment for your USB connection. The most direct connection is the best, without the use of extenders, USB hubs, and USB extension cables.
NOTE: USB Protocol is common on both MAC and Windows computers. The USB generation of your computer will depend on its age - and which USB generation was most prevalent at the time it was manufactured. It is also common for newer computers and laptops to have multiple port types (for example both USB Type A and Type C ports). Although newer and smaller laptops have opted for the USB-C port for its smaller port size. This has made the usage of USB adapter cables and converters commonplace, though, in the case of USB audio, the usage of adapters will not affect the data transfer rates. It is always recommended that you connect your music source directly to your audio equipment for your USB connection. The most direct connection is the best, without the use of extenders, USB hubs, and USB extension cables.
Are USB Audio Cables Different from Regular USB Cables?
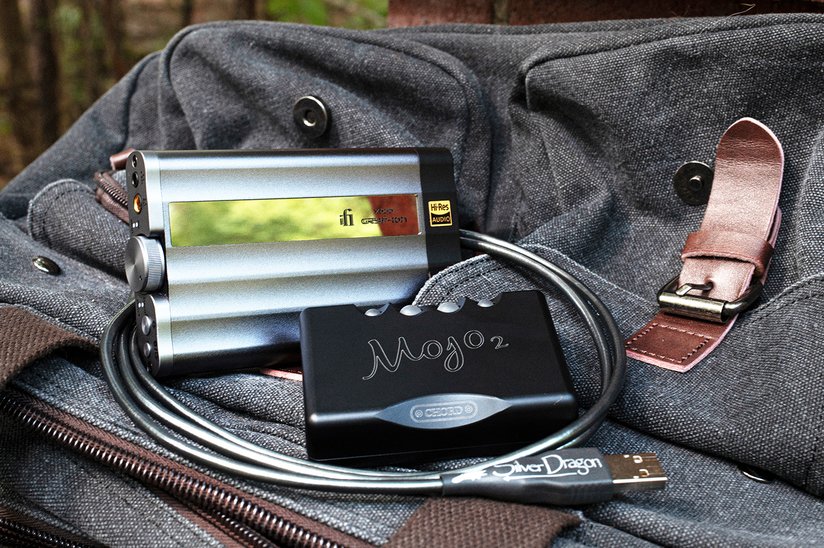
There's an important distinction to make when it comes to audio-specified USB cables. Audio USB cables like Moon Audio's Silver and Black Dragon USB Cables are not meant for usual data transmission in the way that you would connect a hard drive to your computer. This is why USB audio cables will not work for high-speed/superspeed data migration or fast-charging applications. Each connector type has a specific amount of pins that the conductors are attached to. USB Type A is different from C, lightning cables, and an HDMI cable is different from DisplayPort, VGA, and more. Audio cables do not need all the pins for data that usual USB cables utilize. We typically use 4-5 pins for audio transfer, which is all you need. More pins mean faster rates, more data, more conductors, and more expensive cables.
When we say that a USB cable is meant for audio transmission only, this means that the cable should only be used for connecting your source to a DAC or music streamer (just as an example). The only thing that should be transmitted through the cable is your audio data. You might ask, why would I get a cable that only does audio when I can get a stock USB cable that does everything? Answer: the same reason why audiophiles and music lovers buy a standalone DAC, or a high-end preamplifier or music streamer. The fact is that a standalone device or devices meant to do one thing, perform better than do-it-all devices. Better materials, better quality construction, and the fact that something was designed specifically for one purpose means the same thing for cables. In this case, creating and configuring a cable for specific USB audio needs means that it will do that job much better than a standard mass-produced cable made with bad materials.
Materials matter, and that's an important part of the equation for audio. Dragon USB Audio Cables are not designed to be used as hard drive cables, because the transfer speeds are not meant for high-capacity data transfer. High-transfer data speeds use more pins and conductors in a cable to be able to more efficiently more lots of data from point A to point B. Dragon USB Audio Cables are designed with only the conductors and pins necessary to transmit audio data. If a typical USB 3.0 cable connector (any type - USB-B male, micro USB cable, mini USB, USB-C male cable, micro-B cable. Type A male, USB A male - there are a plethora of ways to refer to the naming scheme) has 24 pins, that means we'd have to have 24 conductors of UP OCC silver and copper, and that adds up resulting in really expensive cables. On average it takes 4-5 pins for an audio-spec USB cable.
Audio Only Needs USB 2.0 for Data Transfer - It Will Not Benefit From Newer USB Technology
"Most USB audio interfaces are USB 1.0 and USB 2.0 compatible, so you should have no problem getting a device to work with any computer manufactured in the last 5 years. A USB audio interface attaches to the computer with a standard USB connector and to the device itself with any number of other connectors, ranging from proprietary connections to standardized connections. USB Audio devices do not need the bandwidth of USB3.0 and USB3.0 is backward compatible with USB2.0. USB 2.0 can handle a bandwidth of 480 MB/second. To put this into perspective, 24-bit/192 kHz audio–the highest bandwidth in commercial use–uses approximately 10 MB/second per track of audio. So, a stereo recording would take approximately 20 MB/second or 5 percent of the possible USB 2.0 bandwidth. This large amount of bandwidth available allows for USB audio interfaces to accommodate just about any recording or playback scenario imaginable." -NuPrimeAudio
What Is the Most Important Thing About A USB Cable?
The most important thing about USB is the geometry of the cable itself: the quality, length, shielding, and more. Long cable lengths produce a large resistance, so the shorter the cable, the less distance the data has to run and therefore less resistance in getting to its desired destination. Shielding is extremely important too, because copper and silver conductors act as antennas and will pick up any noise they can if not shielded properly - thus resulting in added noise and interference with your music. We over-shield our Dragon Cables for this very reason. If the cable is too long, or the geometry isn't perfect (which causes interactions in the electrical field that can result in more issues), or the cable isn't shielded properly - all these things can lead to what is called data packet loss.
The most important thing about USB is the geometry of the cable itself: the quality, length, shielding, and more. Long cable lengths produce a large resistance, so the shorter the cable, the less distance the data has to run and therefore less resistance in getting to its desired destination. Shielding is extremely important too, because copper and silver conductors act as antennas and will pick up any noise they can if not shielded properly - thus resulting in added noise and interference with your music. We over-shield our Dragon Cables for this very reason. If the cable is too long, or the geometry isn't perfect (which causes interactions in the electrical field that can result in more issues), or the cable isn't shielded properly - all these things can lead to what is called data packet loss.
What is Packet Loss?
Q: What is Packet Loss?
A: Packet loss occurs when audio data from your source does not reach its destination. A primary cause of this is poor cable geometry and faulty materials. For example, if some of your music data from an external hard drive does not reach the music streamer you are playing it on will result in packet loss. You can run into further clocking and jitter issues when this happens.
A: Packet loss occurs when audio data from your source does not reach its destination. A primary cause of this is poor cable geometry and faulty materials. For example, if some of your music data from an external hard drive does not reach the music streamer you are playing it on will result in packet loss. You can run into further clocking and jitter issues when this happens.
When data gets transferred from point A to point B it gets sent in a measurable called a packet. A packet is a small unit of data that gets sent between an origin or source and the destination. So in this case, it would be the audio data from your hard drive to a music streamer, or from your computer to an external DAC. Packet loss happens when one or more of these packets fail to reach their destination. This results in performance loss in most applications, but when it comes to digital audio data there can arise inconsistencies and issues with the audio and overall quality. This is where people start to run into clocking and jitter issues. Your audio suffers in the end, so minimizing packet loss is critical for high-resolution audio scenarios.
The best way to combat packet loss is to make sure you are using quality USB cables that are made with pure materials and consistent geometries. As we already stated, damaged or faulty cables can invite interference in the signal, which results in noise, audio artifacts, and data loss. Using shorter cable lengths, pure materials, quality geometries, and proper shielding helps ensure that data packets get to where they belong when they need to. Cheap and stock cables are notorious for subpar performance in this regard, so make sure you are prioritizing the quality of your cables just like you are for the gear itself. Your gear is only as strong as the weakest link, and most of the time that's your stock cables.
If you're experiencing packet loss with high-resolution audio, you're not hearing all of your music! It is extremely important that all the data gets to its designated location for high-resolution audio playback. Hi-res audio contains a LOT of data compared to streaming low-res MP3s, and poor quality materials and construction can limit the amount and speed that data transfers; especially with larger data amounts and longer cable lengths. Packet loss might even be considered more prevalent in networking, and considering streaming high-resolution audio takes much more bandwidth and requires more stable connections, the quality of your network cables should be considered in much the same way as your USB Cables. In networking scenarios, faulty or damaged ethernet cables can cause network connection issues resulting in packet loss. It's important to make sure both your USB cables and network cables are made well and in good condition to minimize these issues.
OTG USB Cables and Why You Need Them
Q: What is OTG?
A: OTG stands for "On-the-Go" and is a standard on many Android devices that allows them to act as a host for external devices. This allows you to connect additional devices for expanded utility and functionality. Not all USB cables are OTG, so be sure if you need one that it is built to OTG specs.
A: OTG stands for "On-the-Go" and is a standard on many Android devices that allows them to act as a host for external devices. This allows you to connect additional devices for expanded utility and functionality. Not all USB cables are OTG, so be sure if you need one that it is built to OTG specs.
USB On-The-Go (OTG) is a standard available on many Android phones that allows portable devices to act as USB hosts. This is a great way to expand the utility of your smartphone or tablet. OTG protocol allows you to be able to connect external devices like a storage drive, camera, mouse, and keyboard to your smart device.
The real benefit of this comes with transferring data. Before the OTG protocol, you would have to connect your phone to your laptop or computer, connect the external drive, flash drive, or SD card to the same computer, and initiate the data transfer through the computer. It was a tedious and time-consuming process.
The real benefit of this comes with transferring data. Before the OTG protocol, you would have to connect your phone to your laptop or computer, connect the external drive, flash drive, or SD card to the same computer, and initiate the data transfer through the computer. It was a tedious and time-consuming process.
With USB OTG, you can now connect the external drive directly to the smartphone or tablet, in which case the device would act as a host (like the computer in the previous example), and transfer the data directly without the use of a middleman. It's a more efficient and easier way to transfer data to your device. In order to use OTG you'll need a suitable cable or adapter from your external device to your phone or tablet. There are lots of options here, and you'll need to make sure that your devices can support OTG for this process. If you have any questions feel free to Contact Us and we'll be more than happy to help guide you through this process.
Apple's mobile devices don't offer proper support for USB OTG. You can still connect some external storage devices to your iPhone or iPad, though, as they come pre-equipped to transfer data from external storage devices - as long as you have a compatible lightning or USB-C cable or adapter. If you need an OTG cable for your device, be sure to check out our Silver Dragon USB or Black Dragon USB cables and select the OTG connection types!
How to Buy USB Audio Cables
Q: Do I need a high-quality USB Audio cable?
A: Materials matter. A Ferrari will outperform a Toyota Corolla. A cable made with pure materials, quality construction, and superior shielding will outperform your stock USB cable in the very same way. Make sure that the cable you need is compatible with the product(s) you're using it with and that it meets the data transfer and/or charging speeds that you require.
A: Materials matter. A Ferrari will outperform a Toyota Corolla. A cable made with pure materials, quality construction, and superior shielding will outperform your stock USB cable in the very same way. Make sure that the cable you need is compatible with the product(s) you're using it with and that it meets the data transfer and/or charging speeds that you require.
There's always a need for more USB cables it seems like, and there are a number of things we look for in high-end cables. Things like cable geometries are important to consider because if the materials aren't pure, then you can run into issues like packet loss (mentioned previously). Shielding, or rather proper shielding is also very important because it helps reduce noise and interference - something you definitely do not want in your cable when it comes to pristine audio. At the end of the day, materials matter.
When it comes to USB and backward compatibility, cables can typically be used for different devices. But when it's time to get a new cable or you need something for a special connection option, it's easy to go online and just buy the cheapest option available. As we've already talked about, cheap cables can lead to a myriad of issues. Poorly made cables can be extremely faulty with charging speeds and unreliable performance. Sometimes cables can be made with geometric inconsistencies or bad shielding, and in some cases, they can cause fires. The other factor is that cheap cables are not made to last. I'd argue that the average consumer doesn't take care of their devices like an audiophile or computer/tech-savvy individual.
When it comes to USB and backward compatibility, cables can typically be used for different devices. But when it's time to get a new cable or you need something for a special connection option, it's easy to go online and just buy the cheapest option available. As we've already talked about, cheap cables can lead to a myriad of issues. Poorly made cables can be extremely faulty with charging speeds and unreliable performance. Sometimes cables can be made with geometric inconsistencies or bad shielding, and in some cases, they can cause fires. The other factor is that cheap cables are not made to last. I'd argue that the average consumer doesn't take care of their devices like an audiophile or computer/tech-savvy individual.
If you're looking for new cables for a specific device, you'll need to also make sure that it's compatible with the matching charger if you are planning on using it for charging specifically. Not all cables are rated for PD or high-speed charging, and if they meet too much resistance, can get hot enough to damage your device or cause a fire.
Sometimes the quality of the connector or the configuration of the pinouts can also cause damage to your devices. For instance, the Nintendo Switch gaming console uses a proprietary USB-C pinout, and is recommended that users only purchase licensed Nintendo-branded chargers. There have been countless documented accounts of Switches getting bricked from using third-party docks and charging cables. Your cables aren't throw-away devices and can directly affect the performance and protection of your device. Always make sure that the chargers and devices that you are plugging your USB cables into are rated correctly and are compatible with the charging and power requirements parameters. Cables with higher-quality materials will perform better than ones with subpar materials, but you'll still need to pay attention to device and charging specifications.
Moon Audio OTG Cable Options
Dragon Cables
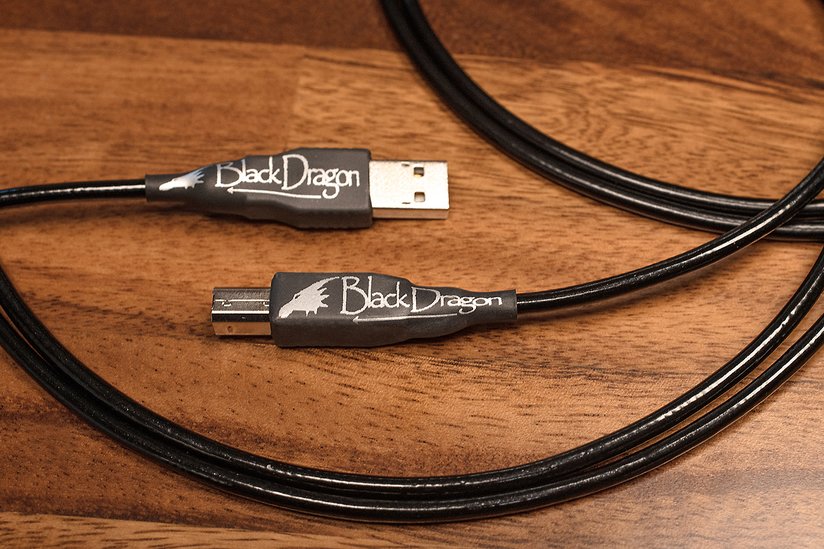
Your gear is only as good as its weakest link, and in most cases, it's the stock USB and audio cables. Companies just don't put the R&D into their cables like they do for the device. That being said, the Silver Dragon USB cable is a higher-quality cable than your OEM option and is built to spec with premium materials and components. If there was a Best Dragon Cables of 2023 list the Silver Dragon USB would be number one. Year after year this is our top-selling Dragon cable. Why is a quality USB cable important for your DAP and other audio gear? Well because they can be used as a high-quality source for your DAC in your home system. It can take the place of a computer to be used as your server and streamer. Some DAPs are even Roon Endpoints. And vice versa - these can also be used as headphone amps & DAC for your laptop when you are working remotely. There are a lot of reasons why you need to make sure your USB cables are not afterthoughts, no matter what source device you are plugging them into.
Our audio cables bring out more of what you love in your music and audio gear. If you love your headphones but wish they had a bit more top-end sparkle - a Silver Dragon headphone cable would be a great option. If your USB cables keep dying - as many stock cables do - then check out our quality USB audio cables. We say time and time again that materials matter, and our audio cables and custom geometries actually help to bring out those desired properties in your gear and music. We make tons of custom options for our customers so that you can get the right HiFi Audio cable for your exact needs. If you have any questions feel free to Contact Us and we'll be more than happy to help.
Generally, stock audio cables are manufactured with subpar materials, metals with impurities, poor geometries, and an overabundance of layers to make them look and feel like a fire hose. Inconsistency and lack of quality control in stock cables can lead to poor sound quality and a veiled sound vs. what the musician intended for you to hear and feel from the music. Dragon cables are handcrafted with the highest standards and made to order according to your specific needs. At Moon Audio, we create a Custom HiFi Audio Cable for you using the highest quality UP-OCC silver or copper conductors that can be manufactured. UP-OCC metals are void of impurities and are optimized for signal transfer and sound quality. We have one of the largest collections of audio and headphone connection options available online and we create limitless audio cable options depending on your specific gear and needs.
Why Dragon Cables?
You’ve heard the saying that a chain is only as strong as its weakest link, right? Well, the same applies to your brand-new audiophile-grade headphones or other audio components. The weakest link, in this case, is your stock cable or the cheap interconnects the manufacturer threw in the box just to get you up and running. Why is the cable always an afterthought, when it’s just as important as the rest of your system? At Moon Audio, we use the best raw materials in our cables to unveil your music. We believe the materials matter and your audio cables should have the same care and craftsmanship that manufacturers put into their audio components and headphones. Audio cables are ultimately the connection to your music. The fact remains that cabling is often considered the last priority to that of the main product and a means to cut down the overall production costs. It’s as simple as that.
Verdict
If you want the best for your audio, then don't settle for a stock cable. At Moon Audio we only make our audio cables with UP-OCC copper and silver strands, quality shielding, and always made-to-order and handcrafted in our headquarters in Cary, North Carolina. Our Black and Silver Dragon USB audio cables will help your high-resolution audio perform with stunning detail and resolution. There are countless reasons why a USB audio cable made with better materials, better geometries, better construction, better shielding, etc, will perform better than a cable with subpar materials, poor shielding, faulty geometries, and more. Bad audio cables can lead to a number of issues for your audio quality, from packet loss to audio artifacts and cutouts. When you're an audiophile or music lover, these issues are simply unacceptable.
The bottom line is that USB audio cables get your audio data from point A to point B, and depending on the quality of that cable you'll find lots of variety as how to well it does the job. This is why you should always opt for a more quality USB or audio cable than what comes packaged in the box of your audio gear. USB technology and cables have been around for a long time, resulting in a variety of data transfer and charging speeds, connector types, and cable lengths to consider when picking out a USB cable. There are a couple of things to keep in mind when shopping for a good USB audio cable. Be sure that you are using a cable designed specifically to be compatible with your device - it's easy enough to find the right connector to the right port, but you'll also need to consider charging requirements and data speeds to prevent the risk of damaging the device or experiencing poor performance. Remember - USB audio cables are not meant to be used for high-speed large data transfers or superspeed charging! Our USB Dragon Cables are built specifically to USB audio specifications, so you can be sure every data packet is reaching its destination when it's supposed to with no added interference. That means pristine audio quality - nothing getting in the way of you and your music.
As an in-house, high-quality cable manufacturer, feel free to Contact Us with any questions that you might have. If you need a custom cable solution we have one of the largest collections of cable connectors around and we'll be more than happy to assist you however we can. Your music deserves better than a stock cable, so it's time to unleash the true potential of your audio. Be sure to check out USB Dragon Audio Cables for the best performance in digital transmission.
Featured Products
Related Videos
Best Portable DACs of 2023
We Answer Your FAQs on DACs
Cables & Coffee, Ep 5: Dragon USB Cables

































