USB Cables: How to Identify Which One You Need

TL;DR: Decoding the Differences between USB C, USB B and USB A
In today's digital age, we find ourselves surrounded by a multitude of devices that rely on USB cables for power, data transfer, and connectivity. From smartphones and laptops to external hard drives, gaming controllers, or wireless headphones, USB cables have become an indispensable part of our daily lives. However, with the ever-evolving USB standards and the various types of cables available, it can be challenging to keep track of which cable is suitable for a specific device.
USB, short for Universal Serial Bus, has come a long way since its introduction in the late 1990s. Over the years, USB has undergone several revisions, each bringing improvements in speed, power delivery, and functionality. As a result, we now have a plethora of USB cable types, such as USB-A, USB-B, USB-C, and more, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. Understanding the differences between these USB cable types is crucial to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with your devices. Using the wrong cable can lead to slower data transfer speeds, inadequate power delivery, or even damage to your valuable gadgets. Moreover, with the increasing adoption of USB-C, which promises to be the universal connector of the future, it's essential to familiarize yourself with its capabilities and limitations.
In this blog post, we aim to provide clarity and guidance on identifying the various USB cable types and their specific uses. We'll dive into the details of each USB standard, explaining its key features, benefits, and drawbacks. By the end of this article, you'll be equipped with the knowledge to confidently choose the right USB cable for your devices, whether you're charging your smartphone, transferring data between your computer and an external drive, streaming music to your high-end audio system/server, or connecting peripherals to your laptop. So, let's untangle the USB cable conundrum together and discover the world of USB connectivity!
USB Type-A
USB Type-A is the most common and recognizable USB connector type. It has been widely used since the introduction of USB technology in the late 1990s. The USB Type-A connector is flat and rectangular in shape, measuring approximately 12mm x 4.5mm.
Key characteristics and uses of USB Type-A:
- Compatibility: USB Type-A ports are found on most computers, laptops, gaming consoles, music servers, and other devices, making it the most universally compatible USB connector.
- Device connection: USB Type-A connectors are used to connect various peripherals to a host device, such as keyboards, mice, external hard drives, flash drives, printers, and more. Type A connectors are also common among device chargers, like phones that come with a USB Type-A charging cable and charger (with a Type-A port).
- Power delivery: USB Type-A ports can provide power to connected devices. However, the power output is limited compared to newer USB standards. USB 3.0 Type-A ports can deliver up to 900mA, while USB 2.0 Type-A ports can deliver up to 500mA.
- Data transfer: USB Type-A connectors support data transfer rates that vary depending on the USB version:
- USB 1.1: Up to 12 Mbps
- USB 2.0: Up to 480 Mbps
- USB 3.0: Up to 5 Gbps
- USB 3.1: Up to 10 Gbps
- Durability: USB Type-A connectors have a lifespan of around 1,500 insertion cycles, which is lower compared to newer connector types like USB-C.
- Orientation: USB Type-A connectors are not reversible, meaning they can only be inserted into a port in one orientation. This can sometimes lead to frustration when trying to plug in a device correctly on the first attempt.
Despite the introduction of newer USB connector types, USB Type-A remains prevalent due to its widespread compatibility and extensive use in existing devices. Many audiophile-grade gear like music streamers and servers use the Type-A variant for external storage connection. You'll sometimes see multiple ports on the back of the music streamer allowing for hard drives or flash drives to be connected.
USB Type-B
USB Type-B is another common USB connector type, typically used for connecting larger peripheral devices to computers or host devices. The USB Type-B connector has a squarish shape with beveled corners on the top, measuring approximately 7.5mm x 8mm.
Key characteristics and uses of USB Type-B:
- Device connection: USB Type-B connectors are commonly found on devices that require a higher power draw or faster data transfer rates, such as external hard drives, printers, scanners, DACs, and audio interfaces.
- Durability: USB Type-B connectors are designed to withstand frequent plugging and unplugging, making them suitable for devices that are regularly connected and disconnected.
- Power delivery: USB Type-B ports can draw more power compared to USB Type-A, with USB 3.0 Type-B ports capable of delivering up to 1.8A.
- Data transfer: USB Type-B connectors support the same data transfer rates as USB Type-A, depending on the USB version:
- USB 1.1: Up to 12 Mbps
- USB 2.0: Up to 480 Mbps
- USB 3.0: Up to 5 Gbps
- USB 3.1: Up to 10 Gbps
- Variants: There are several variants of the USB Type-B connector, including:
- Standard USB Type-B: Used for devices like printers, scanners, and audiophile-grade devices like DACs (Chord Qutest) and music streamers (Matrix Audio X-SABRE 3).
- Mini USB Type-B: This smaller version is used for older mobile devices, digital cameras, and MP3 players/music players (DAPs).
- Micro USB Type-B: An even smaller version used for smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices before the widespread adoption of USB-C.
- Orientation: Like USB Type-A, USB Type-B connectors are not reversible and can only be inserted in one orientation.
USB Type-B connectors are less common compared to USB Type-A, as they are primarily used for specific peripheral devices that require a more robust connection or faster data transfer speeds. Since high-resolution audio does not require high data transfer speeds of USB 3.0 and higher, many manufacturers choose to still use the USB Type B connector for a more secure fit. This is common among audiophile-grade music streamers (like the Matrix Audio X-SABRE 3) and high-end DACs (like the Chord Qutest).
USB Type-C
USB Type-C, or USB-C, is the latest and most advanced USB connector type. It was introduced in 2014 with the USB 3.1 standard and has since gained widespread adoption due to its versatility, high performance, and user-friendly design. The USB-C connector has a small, oval shape and measures approximately 8.4mm x 2.6mm.
Key characteristics and uses of USB-C:
- Reversibility: One of the most significant advantages of USB-C is its reversible design, allowing users to insert the connector in either orientation, eliminating the frustration of incorrect insertion attempts.
- Versatility: USB-C is designed to be a universal connector, capable of delivering power, transferring data, and transmitting video and audio signals, all through a single port.

- High power delivery: USB-C supports USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) specification, enabling it to deliver up to 100W of power. This allows USB-C to charge not only smartphones and tablets but also laptops and other power-hungry devices. Many newer music players (DAPs) and wireless headphones support faster charging speeds due to the newer USB Type-C connectors.
- Fast data transfer: USB-C connectors support USB 3.1 and later standards, offering data transfer speeds up to 10 Gbps (USB 3.1 Gen 2) and 20 Gbps (USB 3.2 Gen 2x2). This makes USB-C ideal for transferring large files, such as high-resolution photos and videos.
- Alternate Mode: USB-C's Alternate Mode feature allows it to support various display protocols, such as DisplayPort and HDMI, enabling users to connect external monitors or TVs directly through the USB-C port.
- Thunderbolt compatibility: Some USB-C ports also support Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4, which offer even faster data transfer speeds (up to 40 Gbps) and the ability to connect multiple high-resolution displays.
- Durability: USB-C connectors are designed to withstand at least 10,000 insertion cycles, making them more durable than previous USB connector types.
USB-C is rapidly becoming the standard connector for a wide range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, desktop computers, and various peripherals. Its versatility, high performance, and user-friendly design make it an ideal choice for both consumers and manufacturers, simplifying connectivity and reducing the need for multiple cable types.
USB Connector Combinations
In the vast ecosystem of USB cables, there are numerous combinations designed to cater to various devices and purposes. Understanding these combinations is essential for ensuring that you have the right cable for your specific needs, whether you're charging your smartphone, transferring data between devices, or connecting peripherals to your computer. It's usually never as easy as "This is a USB type A cable." You have a source end and a receiving end, and there are lots of combinations in between - so let's explore some of the most common USB cable combinations and their uses.
A. USB-A to USB-A
USB-A to USB-A cables, also known as USB extension cables, are commonly used for data transfer between computers or for charging certain devices. These cables have USB Type-A connectors on both ends and are particularly useful when you need to extend the reach of a USB device or when connecting two computers for file sharing.
B. USB-A to Micro USB
USB-A to Micro USB cables are typically used for charging and data transfer with older smartphones, tablets, DAPs, and other portable devices. Before the widespread adoption of USB-C, Micro USB was the standard connector for most Android devices. These cables have a USB Type-A connector on one end and a Micro USB connector on the other, allowing you to connect your device to a computer or wall charger.
C. USB-A to Mini USB
USB-A to Mini USB cables are primarily used for charging and data transfer with older cameras, MP3 players, DAPs, and other electronics. Mini USB was a popular connector type before the introduction of Micro USB and USB-C. These cables have a USB Type-A connector on one end and a Mini USB connector on the other, enabling you to connect your device to a computer or charger.
D. USB-A to USB-C
USB-A to USB-C cables are becoming increasingly common for charging modern smartphones, tablets, laptops, music players, and other devices, as well as for data transfer. These cables have a USB Type-A connector on one end and a USB-C connector on the other, allowing you to connect your USB-C device to a computer or wall charger that has a USB Type-A port. USB-C charging cables come with most consumer devices today like the iPad Pro, Samsung smartphones, Mac, Macbook Pro, and even some Windows PCs with PD charging capabilities.
E. USB-C to USB-C
USB-C to USB-C cables are found in newer devices and are often used for fast charging and high-speed data transfer between compatible devices. These cables have USB-C connectors on both ends, enabling you to connect two USB-C devices or to charge your USB-C device using a USB-C power adapter. USB-C to USB-C cables are capable of delivering higher power and faster data transfer speeds* compared to other USB cable combinations.
F. USB-C to Lightning
USB-C to Lightning cables are exclusive to Apple devices and are used for charging and data transfer between newer iPhones, iPads, and MacBooks. These cables have a USB-C connector on one end and a Lightning connector on the other, allowing you to connect your Apple device to a USB-C power adapter or a computer with a USB-C port. USB-C to Lightning cables offer faster charging speeds compared to the older USB-A to Lightning cables.
G. Differentiating Charging-Only Cables from Those That Support Data Transfer
It's important to note that not all USB cables are created equal. Some cables are designed for charging only and do not support data transfer. These cables are often cheaper and may have lower-quality wiring. On the other hand, cables that support both charging and data transfer have the necessary wiring and shielding to ensure reliable data communication between devices. When purchasing a USB cable, be sure to check the product description or packaging to determine whether it supports data transfer if that is a requirement for your needs.
*All Dragon USB Audio Cables are built to audio data transfer specifications. Since high-resolution audio data transfer does not currently exceed USB 2.0 specs, all of our digital audio cables use USB 2.0 speeds. Please note that we do not make video cables.
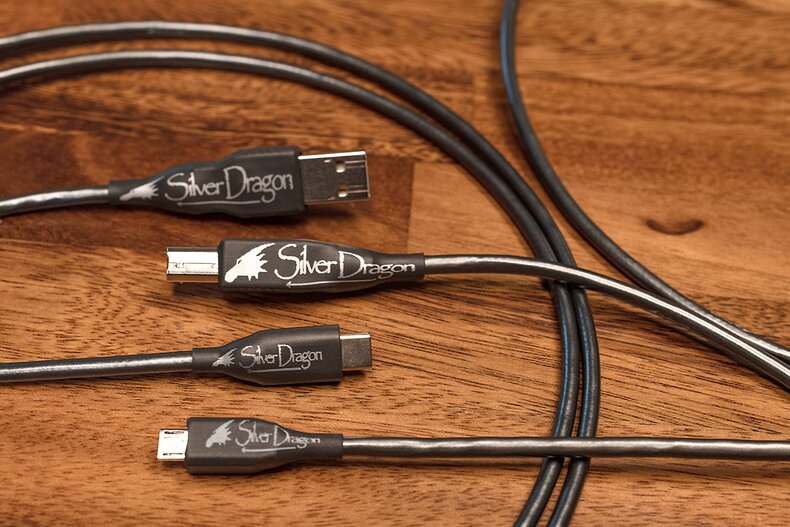
Dragon Audio Cables
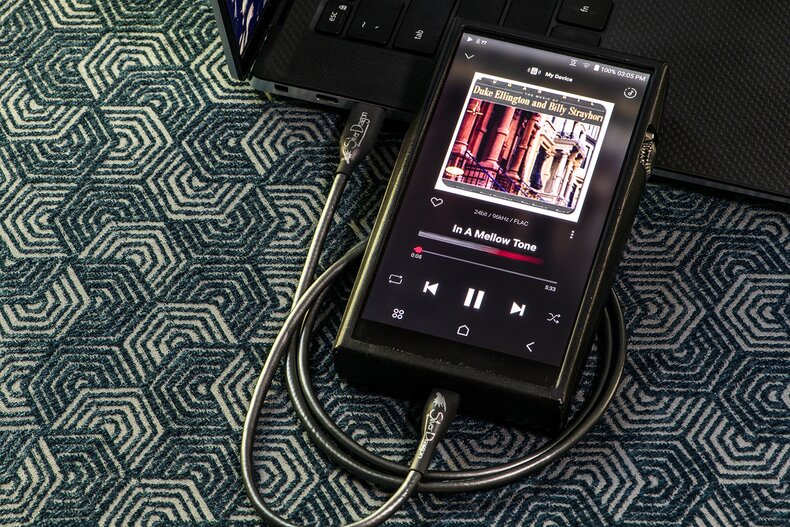
Your gear is only as good as its weakest link, and in most cases, it's the stock USB and audio cables. Companies just don't put the R&D into their cables like they do for the device. That being said, the Silver Dragon Premium USB Cable is a higher-quality cable than your OEM option and is built to spec with premium materials and components. Year after year this is our top-selling Dragon cable. We also have a Black Dragon USB Cable for those who prefer a more musical presentation. There are a lot of reasons why you need to make sure your USB cables are not afterthoughts, no matter what source device you are plugging them into.

Why Dragon Cables?
You’ve heard the saying that a chain is only as strong as its weakest link, right? Well, the same applies to your brand-new audiophile-grade headphones or other audio components. The weakest link, in this case, is your stock audio cable or the cheap interconnects the manufacturer threw in the box just to get you up and running. Why is the audio cable always an afterthought, when it’s just as important as the rest of your system? At Moon Audio, we use the purest and best raw materials in our cables to unveil your music. We believe that materials matter and your audio cables should have the same care and craftsmanship that manufacturers put into their audio components and headphones. Audio cables are ultimately the connection to your music. The fact remains that cabling is often considered the last priority to that of the main product and a means to cut down the overall production costs. It’s as simple as that. Dragon Cables elevate every note - as if you were hearing your favorite music for the very time.
Verdict
Knowing the connectors on USB cables is half the battle in helping to figure out and understand what they do. It's important to correctly identify your USB cables for device compatibility and functionality. The best-case scenario is that you plug it in and it works as desired. The worst case scenario is that you plug it in, fry your device, or worse, even start a fire because your cable is trying to do something it is not built to handle. Sharing is caring when it comes to tech tips, so be sure that if you see something, say something! We know the amount of time and money you put into your audiophile-grade music players and gear, and protecting it is our concern just as much as it is yours.
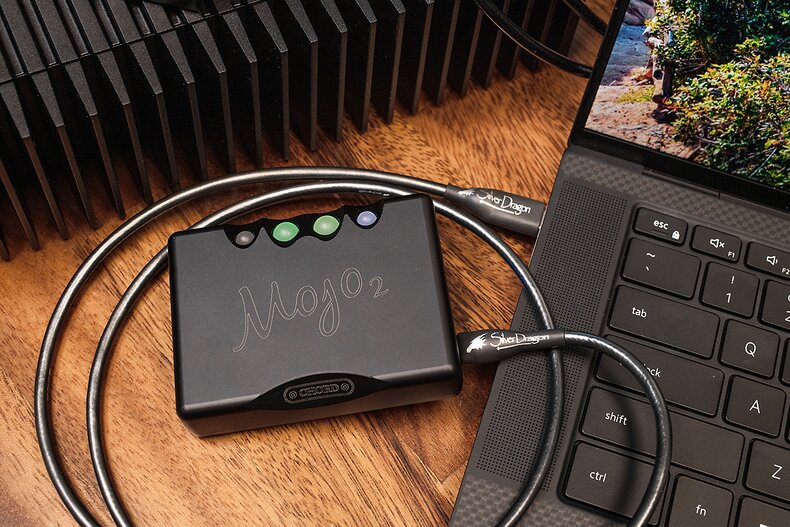
If you're looking for the very best in USB Cables, check out our Silver Dragon Premium USB Cable. As with all of our Dragon Audio Cables, the Silver Dragon Premium is built with care, using only the highest-quality materials you can source. Because of the high-quality materials and cable geometry, our USB Cables will greatly reduce stock USB cable issues such as packet loss and jitter. USB A, USB B, and USB-C connectors are of the utmost highest quality and ideal for mounting high-quality Silver Dragon Premium USB Cables.
Our Silver Dragon USB Cable is our best-selling USB Cable at Moon Audio, offering an extraordinary amount of detail and resolution to your hi-fi system. The Silver Dragon USB Cable is designed to transfer digital audio from your source device (like a computer, phone, tablet, or digital audio player) to a USB-capable DAC. Because of the high-quality materials and cable geometry, our USB cables will greatly reduce stock USB cable issues such as packet loss and jitter.
Before we go, here are some key tips for identifying your USB cables:
- Examining Connector Shapes and Sizes Pay close attention to the shape and size of the connectors on both ends of the cable. USB-A connectors are flat and rectangular, USB-B connectors have a squarish shape with beveled corners, and USB-C connectors are small and oval-shaped. Familiarizing yourself with these distinct shapes will help you quickly identify the cable type.
- Checking Connector Labels or Markings Many USB cables have labels or markings near the connectors that indicate the USB version, speed, or power delivery capabilities. Look for labels such as "USB 3.0," "USB 2.0," or "USB-PD" to determine the cable's specifications.
- Using Online Resources or Manufacturer Documentation If you're unsure about a specific cable, you can often find information online or in the manufacturer's documentation. Websites like USB-IF (USB Implementers Forum) provide detailed specifications and guides on USB standards and cables.
- Consulting Device Manuals or Specifications When in doubt, refer to the manual or specifications of the device you're trying to connect. The manufacturer will typically specify the recommended cable type and any specific requirements for optimal performance.
- Being Cautious of Counterfeit or Non-Standard Cables Be wary of counterfeit or non-standard USB cables, as they may not meet the necessary specifications and could potentially damage your devices. Always purchase cables from reputable sources and check for any signs of poor quality or inconsistencies in the connectors or cable construction.
By following these tips and leveraging your newfound knowledge of USB cables and connectors, you'll be well-equipped to navigate the world of USB connectivity. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a professional, an audiophile, or an everyday user, understanding USB cables is essential in our increasingly digital world. If you have any questions feel free to leave a comment. Happy listening!
Featured Products
Related Videos
USB Audio Cables: Why They're Important
Cables & Coffee, Ep.5: Dragon USB Cables
Best Portable DACs of 2023
FAQ
Q: What are the different versions of USB cables, and what do they mean?
A: USB cables come in various versions, including USB-A, USB-B, USB-C, and micro USB. Each version denotes the connector type and functionality, with USB-C being the most recent and versatile standard.
Q: What is the difference between USB-A, USB-B, and USB-C cables?
A: USB-A cables are commonly used for connecting devices like computers, chargers, and peripherals. USB-B cables are typically found in printers and external hard drives. USB-C cables are reversible and support faster data transfer and charging speeds.
Q: Are USB-C cables compatible with older USB ports?
A: Yes, USB-C cables are designed to be backward compatible with older USB ports, but you may need an adapter or converter to connect them to USB-A or USB-B ports.
Q: Can I use a USB-C cable to charge my device?
A: Yes, USB-C cables are widely used for charging smartphones, laptops, tablets, music players, and other electronic devices. They support fast charging and power delivery capabilities.
Q: What is the maximum data transfer speed of USB cables?
A: The data transfer speed of USB cables varies depending on the version and specifications. USB 2.0 cables typically offer speeds up to 480 Mbps, while USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 cables can reach up to 5 Gbps and 10 Gbps, respectively. Our Dragon USB Audio Cables are built to USB 2.0 specs since the bandwidth required by high-resolution audio files does not exceed the specifications of USB 2.0. This way we can keep our production quality high while keeping costs down for the music lover.
Q: Are all USB-C cables the same?
A: No, USB-C cables can vary in terms of quality, durability, and features. It's essential to choose certified cables from reputable manufacturers like Moon Audio to ensure compatibility and reliable performance.
Q: Can I use a USB-C cable for video output?
A: Yes, some USB-C cables support video output and can be used to connect devices like laptops or smartphones to external monitors or displays. However, not all USB-C cables offer this functionality, so it's essential to check the specifications. Our Dragon USB Audio Cables are built for audio specifications only and do not support video applications.
Q: What is the difference between USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 cables?
A: USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 cables offer similar data transfer speeds, but USB 3.1 cables support additional features like power delivery and alternate modes for video output.
Q: Can I use a USB cable to transfer files between devices?
A: Yes, USB cables are commonly used for transferring files between computers, smartphones, cameras, portable music players, music streamers, and other devices. Simply connect the devices using the appropriate USB cable and follow the on-screen instructions.